The Importance of Clear SaaS Homepage Positioning

How do you know if your positioning is working for you? Right, you don't really know. So how do you improve it? We discussed this with Anthony Pierri from Fletch. He's a positioning expert and has helped over 100 startups improve theirs.
In this webinar (video at the end of this article) we discussed everything positioning. Including the best tips and tricks for improving your homepage. And we broke down a few homepages that people submitted in the chat.
"Most people write home pages for people who already really, really have deep brand recognition."
And of course, we played Who's that SaaS – a game that shows how important it is to get your positioning right. Without it, people simply don't understand what you do. Unless they're already familiar with your brand (e.g. Slack "Where work happens")
Tips to improve your positioning
1. Avoiding Ambiguity
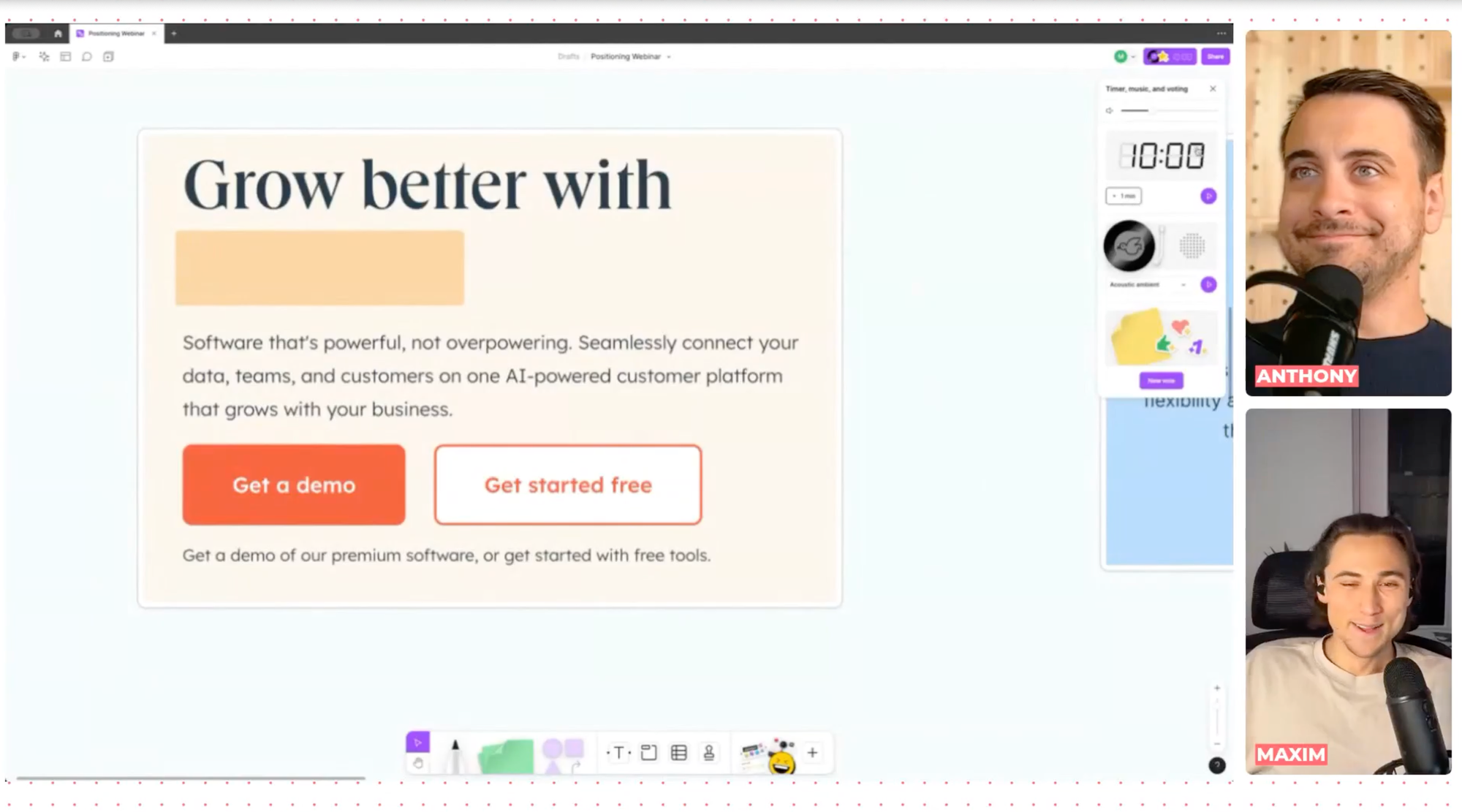
Many SaaS homepages suffer from vague messaging. Phrases like "Grow better with X software" or "Unlock your team's best work" are often too generic. These statements fail to convey the specific value proposition and can leave potential customers confused about what the product actually does.
So be specific while differentiating yourself from the competition.
The Problem with Ambiguity
Ambiguous messaging often stems from the assumption that visitors already have a deep understanding of the brand and its offerings. This can lead to vague, high-level statements that fail to convey the product's specific value. For example, phrases like "Grow better with X software" or "Payroll for global teams" are too broad and do not provide enough context for new users.
Consequences of Ambiguity
- User Confusion: Visitors may leave the site if they cannot quickly grasp what the product does.
- Lower Conversion Rates: Ambiguous messaging can result in lower sign-ups and purchases as users are unsure of the product's benefits.
- Increased Bounce Rates: Users are more likely to bounce if they do not find the information they need immediately.
1. Be Specific About What the Product Does
Instead of using broad, generic statements, clearly articulate the product's functionality. For example:
- Ambiguous: "Grow better with X software."
- Specific: "Enhance your marketing campaigns with X software's AI-driven analytics and automated email marketing tools."
2. Highlight Key Features and Benefits
Directly mention the primary features and how they benefit the user. This helps in setting clear expectations.
- Ambiguous: "All-in-one customer data and analytics."
- Specific: "Combine CRM and CDP functionalities to enrich first-party data, generate AI-driven personas, and activate marketing segments."
3. Use Clear, Descriptive Language
Avoid jargon and buzzwords that may not be immediately understood by all users. Instead, use straightforward language that clearly describes the product.
- Ambiguous: "Seamlessly connected to your data, teams, and customers."
- Specific: "Integrate your CRM, email marketing, and customer support tools into one platform."
4. Provide Context with Examples
Use examples or case studies to illustrate how the product works and its impact.
- Ambiguous: "Powerful, not overpowering."
- Specific: "Our software helps you manage customer data without overwhelming your team, as seen in our case study with Company Y."
5. Address the User’s Pain Points
Identify and address the specific problems your target audience faces and how your product solves them.
- Ambiguous: "Grow faster with our solution."
- Specific: "Reduce customer churn by 20% with our automated follow-up emails and personalized customer journeys."
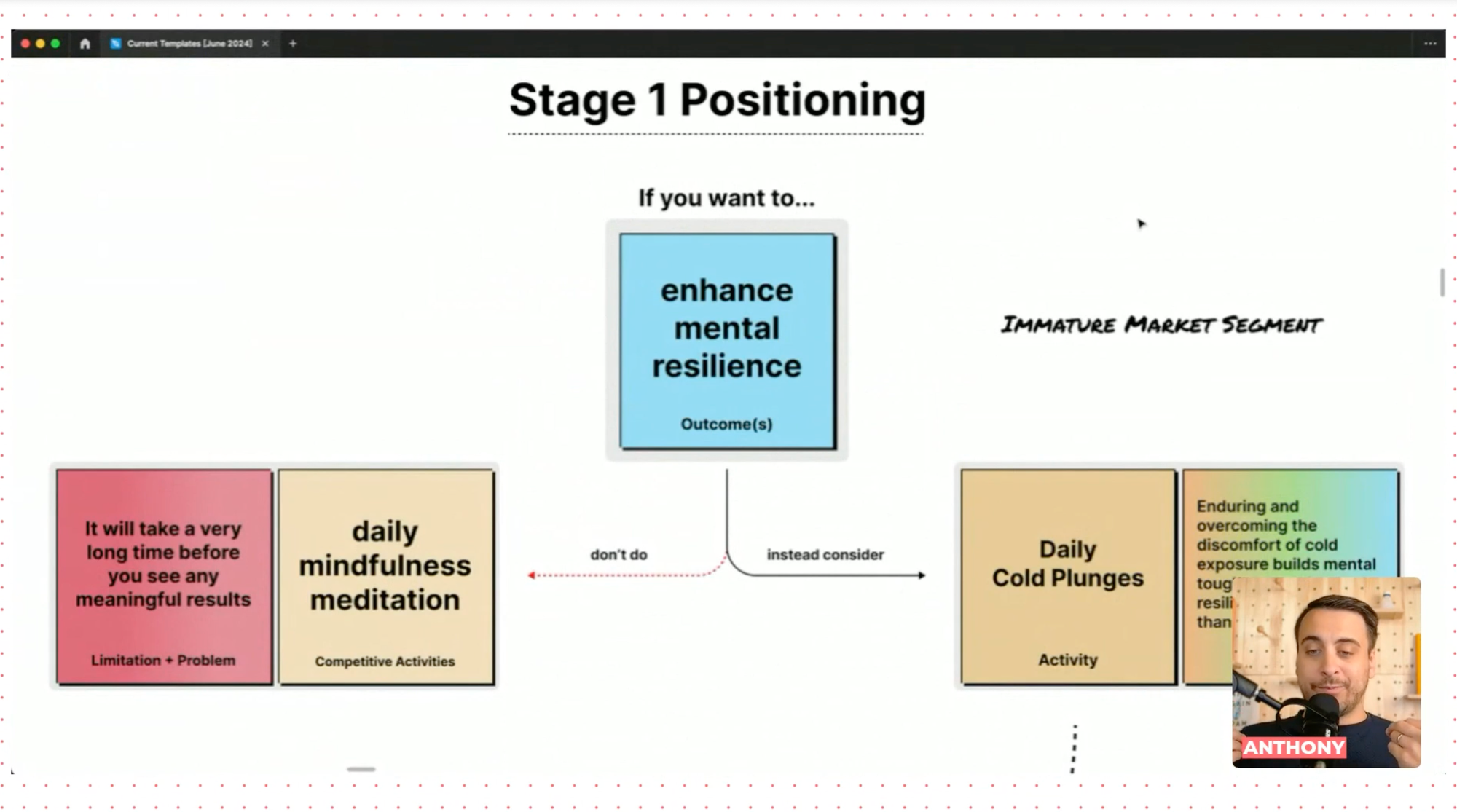
2. Understanding Market Maturity
Positioning should be tailored to the market's maturity stage:
- Immature Market: Focus on educating the audience about the problem and why they need a solution.
- Emerging Market: Highlight why your solution is better than existing methods or tools.
- Mature Market: Emphasize your product's unique features and why it outperforms competitors.
Example:
- Product: Ice Bath for Health Benefits
- Positioning: "Enhance your mental resilience with daily cold plunges. Unlike traditional mindfulness meditation, cold exposure builds mental toughness more rapidly."
2. Emerging Market
In an emerging market, customers are aware of the problem and are beginning to look for solutions. The focus shifts to differentiating the product from other emerging solutions.
Characteristics:
- Growing Awareness: Customers recognize the problem and are seeking solutions.
- Moderate Education Requirement: Some education is still needed, but customers have a basic understanding.
- Increasing Competition: More competitors are entering the market.
Positioning Strategy:
- Differentiate from Alternatives: Highlight how the product is better than other emerging solutions.
- Emphasize Unique Features: Focus on the unique aspects of the product that set it apart.
- Leverage Early Adopters: Use testimonials and case studies from early adopters to build credibility.
Example:
- Product: Ice Bath for Health Benefits
- Positioning: "Experience the benefits of cold exposure with our ice bath. Unlike cold showers, our ice bath provides consistent, intense cold exposure for optimal results."
3. Mature Market
In a mature market, customers are well aware of the problem and the available solutions. The focus is on competing directly with established players and emphasizing superior features and benefits.
Characteristics:
- High Awareness: Customers are well-informed about the problem and the solutions.
- Low Education Requirement: Minimal effort is needed to explain the problem or the solution.
- High Competition: Many competitors with established market presence.
Positioning Strategy:
- Compete on Features and Benefits: Clearly articulate why the product is superior to competitors.
- Highlight Customer Success: Use detailed case studies and testimonials to demonstrate success.
- Focus on Brand Loyalty: Build a strong brand identity to foster customer loyalty.
Example:
- Product: Ice Bath for Health Benefits
- Positioning: "Choose our ice bath for the ultimate cold exposure experience. Trusted by top athletes, our product offers unmatched durability and performance."
Assessing Market Maturity
To determine the maturity of your market, consider the following:
- Customer Awareness: Are customers aware of the problem and the available solutions?
- Competitive Landscape: How many competitors are there, and how established are they?
- Customer Feedback: What do customers say about their understanding of the problem and the solution?
Adapting Positioning Based on Market Maturity
- Immature Market: Focus on education and highlighting unmet needs.
- Emerging Market: Differentiate from other solutions and emphasize unique features.
- Mature Market: Compete on superior features, customer success, and brand loyalty.
3. Targeting the Right Audience
Homepages should be designed with the primary decision-makers in mind. For B2B SaaS, this often means focusing on the needs and pain points of the person most likely to initiate the buying process, such as a manager or team lead.
"You should write the page for the champion, you should position for the person who's gonna be most likely to start the buying process."
4. Clear Value Proposition
Using clear, straightforward language to describe what the product does is crucial. For example, instead of saying "All-in-one customer data and analytics," specify what tools or functionalities are combined and how they benefit the user.
"If you don't have highly differentiated features for the segment, you just might not be able to hang in that segment."
5. Leveraging SEO Without Overdoing It
While incorporating SEO keywords is important, it should not come at the expense of clarity. Keywords like "AI hiring platform" can be used effectively in specific landing pages or content pieces rather than being the main focus of the homepage.
6. Feedback Loops
Regularly gather feedback from various channels—sales calls, user interactions, and marketing analytics—to ensure the homepage messaging aligns with user expectations and needs.
1. Customer Feedback
Direct input from users about their experiences with the product.
Methods:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Collect structured feedback on specific aspects of the product.
- Customer Interviews: Gain deeper insights through one-on-one conversations.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measure customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Benefits:
- Identify Pain Points: Understand the challenges users face.
- Gauge Satisfaction: Measure how well the product meets customer needs.
- Uncover Opportunities: Discover potential areas for new features or improvements.
2. Sales Feedback
Insights from the sales team based on their interactions with prospects and customers.
Methods:
- Sales Call Recordings: Analyze conversations to identify common questions and objections.
- Win/Loss Analysis: Understand why deals are won or lost.
- Sales Team Meetings: Regular discussions to share insights and trends.
Benefits:
- Refine Messaging: Adjust positioning based on what resonates with prospects.
- Improve Sales Strategies: Tailor approaches to address common objections.
- Align Marketing and Sales: Ensure consistent messaging across teams.
3. Product Usage Data
Behavioral data showing how users interact with the product.
Methods:
- Analytics Tools: Track user actions and feature usage.
- Heatmaps: Visualize where users click and spend time.
- Cohort Analysis: Study user behavior over time to identify trends.
Benefits:
- Optimize Features: Enhance features based on actual usage patterns.
- Identify Drop-off Points: Find where users abandon the product and why.
- Personalize Experiences: Tailor the product experience to different user segments.
4. Market Feedback
Information about market trends, competitor actions, and industry developments.
Methods:
- Competitive Analysis: Monitor competitors’ offerings and positioning.
- Industry Reports: Stay updated on market trends and forecasts.
- Customer Advisory Boards: Engage with key customers to gather strategic insights.
Benefits:
- Stay Competitive: Adjust positioning to stay ahead of competitors.
- Anticipate Trends: Prepare for market shifts and emerging needs.
- Validate Assumptions: Ensure that positioning aligns with market realities.
Implementing Effective Feedback Loops
1. Establish Clear Objectives
Define what you aim to achieve with your feedback loops. Objectives could include improving customer satisfaction, refining product features, or enhancing market positioning.
2. Choose the Right Tools
Select tools and platforms that facilitate efficient feedback collection and analysis. Examples include survey tools (e.g., SurveyMonkey), analytics platforms (e.g., Google Analytics), and CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce).
3. Create a Feedback Culture
Encourage a culture where feedback is valued and acted upon. Ensure that all team members understand the importance of feedback and are motivated to contribute.
4. Analyze and Act on Feedback
Regularly review feedback data to identify patterns and insights. Develop action plans to address issues, capitalize on opportunities, and refine positioning.
5. Close the Loop
Communicate back to customers and stakeholders about the changes made based on their feedback. This builds trust and demonstrates that their input is valued.
Positioning into practice: Anthony's Landing Page Reviews
During the webinar we asked people to submit their website for review by Anthony. We reviewed 3 of them. Let's look at how Anthony puts these tips into practice and what he has to say about these websites. Which tips do apply to your website?
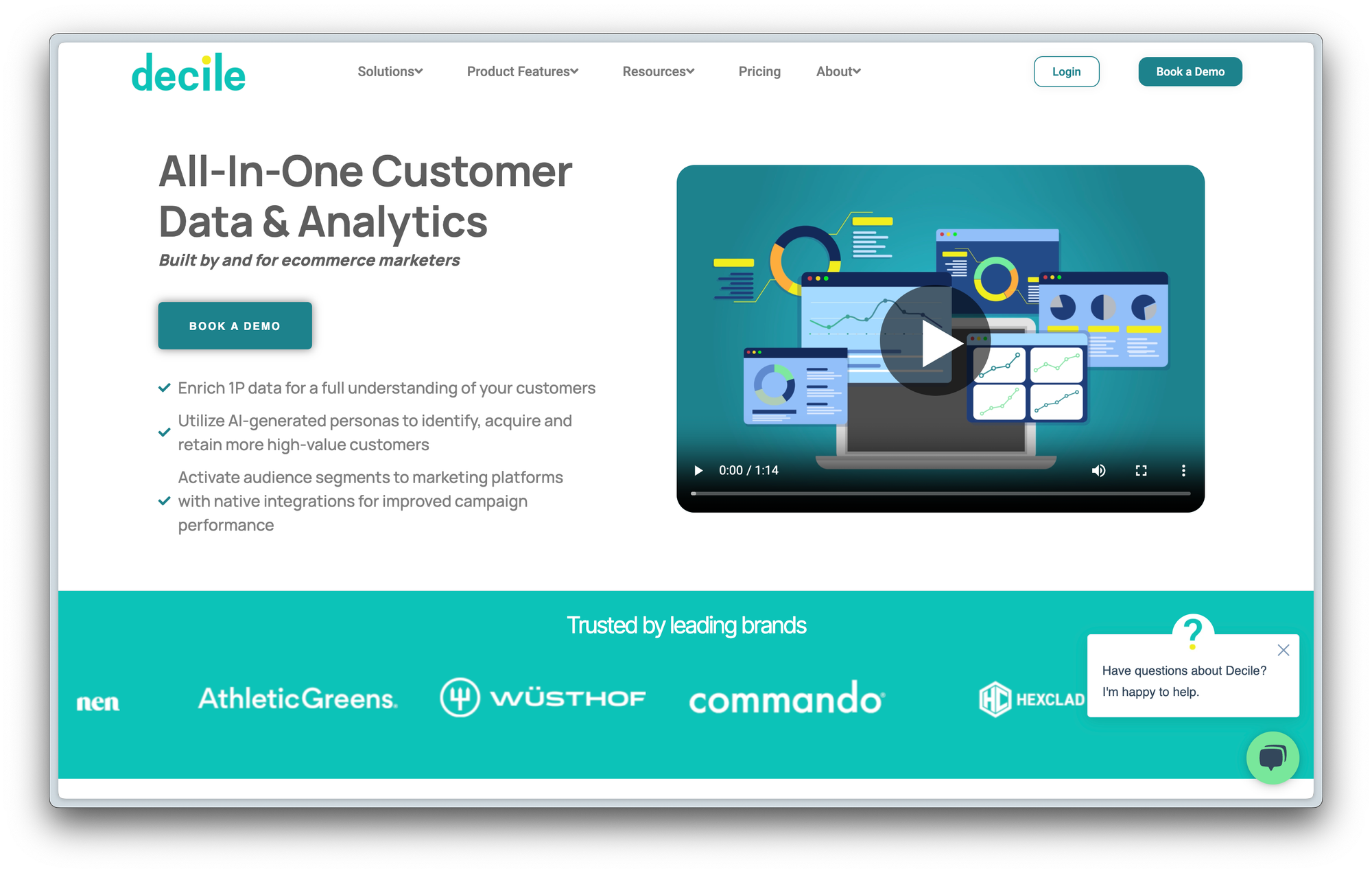
Landing Page 1: Decile
Headline: "All-in-one customer data and analytics built by and for marketers." Subheadline: "Enrich first-party data for a full understanding of your customers. Utilize AI-generated personas to identify, acquire, and retain more high-value customers. Activate segments to marketing platforms with native integrations, a 360 view of your customers."
Anthony's Review
Anthony immediately called out "all-in-one," which he noted can often be vague and unhelpful. It's important to clearly state what specific tools or functionalities are being combined in the "all-in-one" solution. Because if you don't, what's different about all-in-one?
Key Points:
- Clarity: Instead of saying "all-in-one," specify the tools being combined (e.g., CRM, CDP).
- User Effort: Avoid making the user figure out where the product fits in their tech stack.
- Differentiation: Highlight unique capabilities that the all-in-one solution unlocks, which point solutions might not offer.
Recommendations
- Clearly state the specific tools or functionalities that are being combined.
- Highlight unique capabilities and benefits that the all-in-one solution provides.
- Ensure the messaging is straightforward and easy to understand.
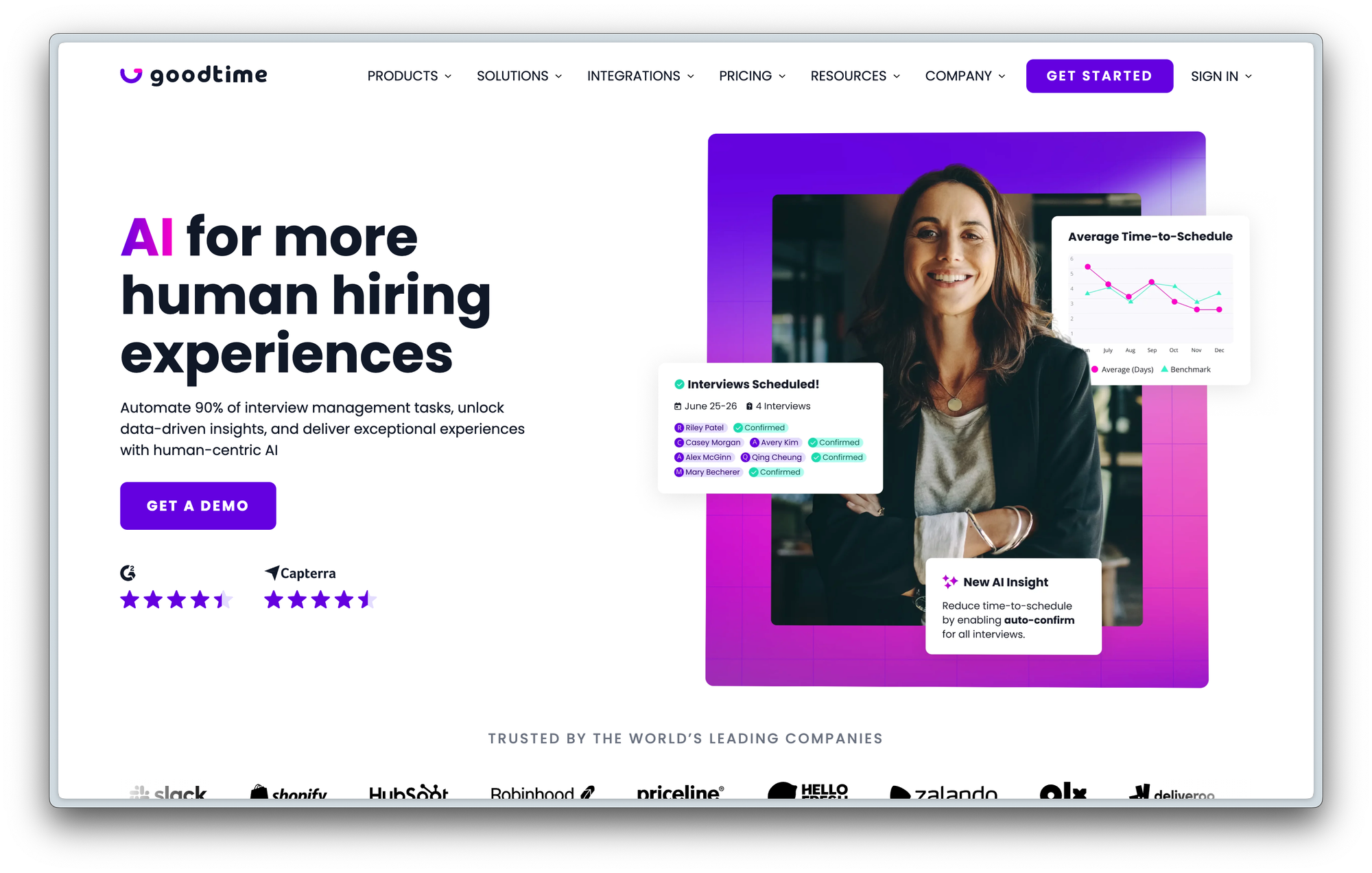
Landing Page 2: GoodTime
Headline: "AI for more human hiring experiences."
Subheadline: "Automate 90% of interview management tasks. Unlock data-driven insights. Deliver exceptional experiences with human-centric AI."
Anthony's Review
Anthony appreciated the clear focus on hiring but pointed out that terms like "deliver exceptional experiences" are too vague. Also here, the page is missing clear benefits and specificity.
Key Points:
- Specificity: Clearly define what "exceptional experiences" means and for whom (hiring managers, candidates, etc.).
- AI Differentiation: Given the widespread use of AI, it's crucial to explain how the AI in this product is unique or superior.
- Target Audience: Position the page for the champion (e.g., hiring manager) who will initiate the buying process.
Recommendations
- Be specific about the benefits and features, avoiding vague terms.
- Clearly explain how the AI differentiates from competitors.
- Focus the messaging on the primary decision-maker or champion within the target audience.
Landing Page 3: Retainful
Headline: "Send emails to convert and sell."
Subheadline: Build an email list. Engage customers at every stage of the journey. Increase your store's revenue."
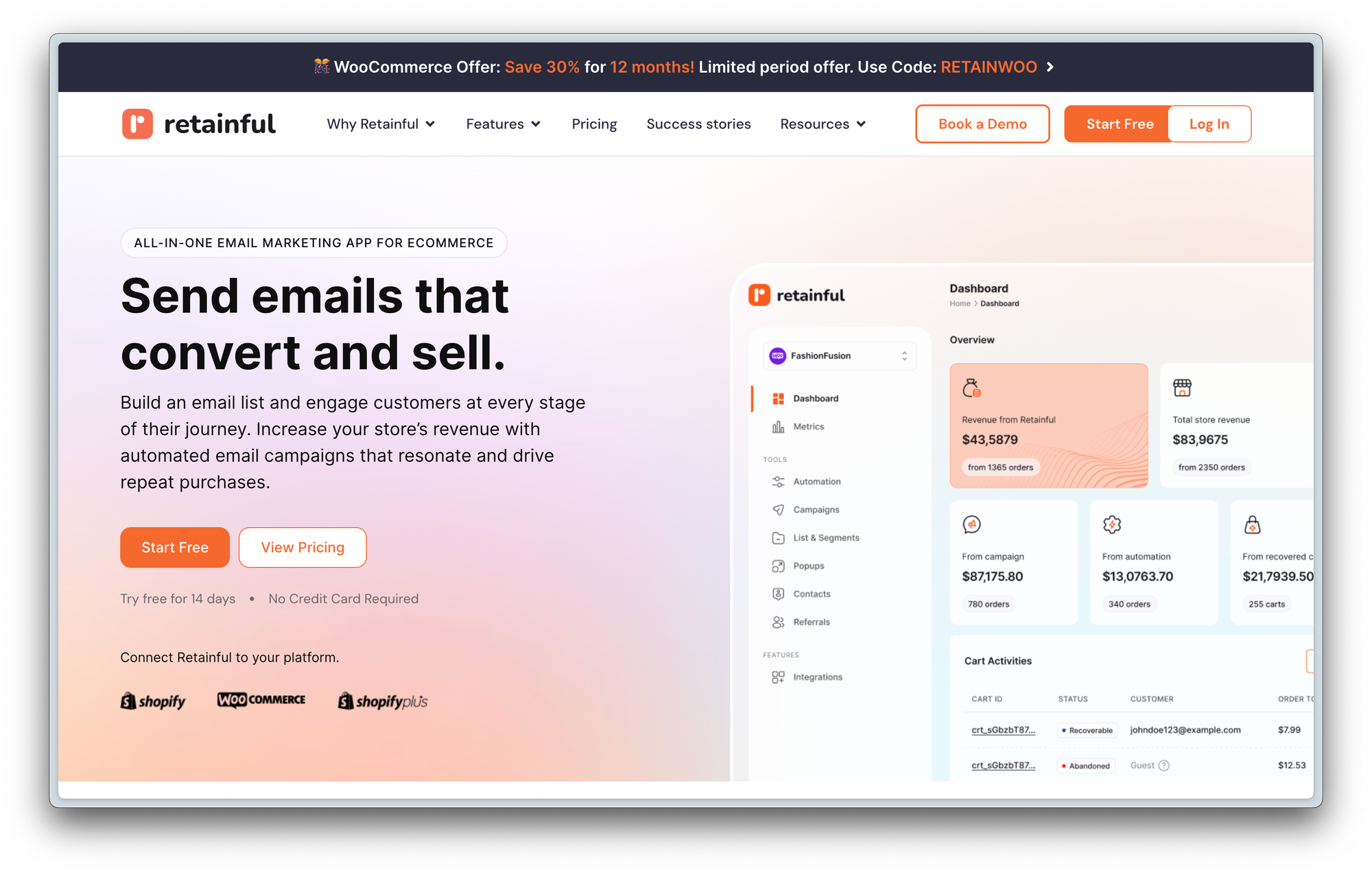
Anthony's Review
Anthony complained about the generic nature of the messaging, noting that it doesn't differentiate the product from other email marketing solutions. He emphasized the need to highlight unique features or benefits that set the product apart.
Key Points:
- Differentiation: Avoid generic claims that apply to all email marketing tools.
- Unique Features: Highlight specific features that make the product stand out (e.g., abandoned cart recovery).
- Target Audience: Ensure the messaging resonates with the specific needs and pain points of the target audience.
Recommendations
- Focus on unique features and benefits that differentiate the product.
- Avoid generic claims and provide specific examples of how the product can help.
- Tailor the messaging to address the specific needs and pain points of the target audience.
Key Takeaways for Effective Landing Pages
- Clarity and Specificity: Clearly state what your product does and avoid vague terms. Be specific about the benefits and features.
- Differentiation: Highlight what makes your product unique and why it’s better than the competition.
- Target Audience: Tailor your messaging to the primary decision-maker or champion within your target audience.
- User Effort: Make it easy for users to understand where your product fits in their tech stack and how it can help them.
Anthony’s reviews provided a masterclass in effective landing page design and messaging. By following these principles, companies can create landing pages that not only attract attention but also convert visitors into customers.
And as you see from these examples, you can almost never be specific enough about what you do differently from your competition. Most of Anthony's feedback was about the positioning not being specific enough – or simply not differentiating enough from the competition.
Who's that SaaS?
To see for yourself how vague positioning can be, let's look at famous companies' their websites. In Who's that SaaS we guess the startup by looking at their hero sections. As you might guess, it's hard to guess which company is behind it. And even more so, it's sometimes impossible to understand what they do.
And that's exactly the reason why positioning is so important. Here's the quiz, feel free to follow along. Correct answers are on the bottom.
Questions and Answers
Question 1
Homepage Copy: "Grow better with X software that's powerful, not overpowering, seamlessly connected to your data, teams, and customers on one AI-powered customer platform that grows with your business."
Commentary:
- Anthony notes the frequent use of AI in the copy.
- He mentions the differentiation between "grow faster" and "grow better," hinting at a competitive landscape.
Question 2
Homepage Copy: "Payroll for global teams. X helps tens of thousands of companies expand globally with unmatched speed, flexibility, and compliance."
Commentary:
- Maxim mentions that all selected pages are from famous tech startups.
- Anthony discusses the clarity of the copy in explaining the product's function.
Question 3
Homepage Copy: "Automate stuff you can type."
Commentary:
- Anthony discusses the simplicity and directness of the copy.
- They mention the competitive landscape and the importance of clear messaging.
Question 4
Homepage Copy: "Make forms worth filling out. Get more data, like signups, feedback with forms designed to be refreshingly different."
Commentary:
- Anthony appreciates the straightforwardness and honesty of the copy.
- They discuss the importance of not over-promising in marketing messages.
Question 5
Homepage Copy: "Plan, organize, play."
Commentary:
- Anthony notes the playful language used, which is unusual for B2B.
- They discuss the importance of branding and font recognition.
Question 6
Homepage Copy: "Respect your data, your AI, your future."
Commentary:
- Anthony and Maxim discuss the abstract nature of the copy.
- They mention the importance of clear and direct messaging.
Question 7
Homepage Copy: "The number one AI work management platform."
Commentary:
- Anthony shares a fun anecdote about wanting to create a standalone game based on this concept.
- They discuss the competitive landscape and the importance of clear differentiation.
Question 8
Homepage Copy: "Where work happens."
Commentary:
- Anthony and Maxim discuss the familiarity of the phrase and its association with a well-known brand.
- They mention the importance of brand recognition.
Question 9
Homepage Copy: "Unlock your team's best work with."
Commentary:
- Anthony expresses his dislike for the vagueness of the copy.
- They discuss the importance of clear and specific messaging.
Question 10
Homepage Copy: "Marketing revolutionized by AI. AI isn't next. It's now. Harness it with X to transform your creative capability, better connect with your customers, and secure the competitive advantage."
Commentary:
- Anthony and Maxim discuss the overuse of AI in marketing messages.
- They mention the importance of clear differentiation and avoiding generic claims.
Answers:
- HubSpot
- Deel
- Zapier
- Typeform
- Notion
- Databricks
- Asana
- Slack
- Jira
- Jasper
Conclusion
Effective homepage positioning in SaaS requires a balance of clear, specific messaging tailored to the market's maturity and the target audience's needs. By avoiding vague statements and using only precise and specific language, companies can better engage potential customers and differentiate themselves in a crowded market.
Don't hesitate to reach out to Anthony if you need help with positioning. And before we forget, if you're running webinars. Run them on Contrast ;-)

